brinell hardness test history|brinell hardness test example : broker The first widely accepted and standardized indentation-hardness test was proposed by J. A. Brinell in 1900. Brinell’s interest in materials science grew during his involvement in a several Swedish iron companies and his . webNapoleon Games Support (Frequently Asked Questions) Need assistance? Find quick answers to all your questions on this support page! Explore the frequently asked .
{plog:ftitle_list}
Resultado da 18 de jul. de 2019 · Explaining the KawaiiBot Hoax. Spoilers: It's all fake, here's why. Update: Discord themselves have already confirmed that .
The Brinell hardness test was developed by Swedish engineer Johan August Brinell in 1900. Brinell, who was actively involved in the Swedish iron industry. His aim was to create a reliable and standardized method for . The first widely accepted and standardized indentation-hardness test was proposed by J. A. Brinell in 1900. Brinell’s interest in materials science grew during his involvement in a several Swedish iron companies and his .Brinell hardness is determined by forcing a hardened steel or carbide ball of known diameter under a known load into a surface and measuring the diameter of the indentation with a .
water vapor permeability test method factories
August Brinell (19 June 1849 – 17 November 1925) was a Swedish Metallurgical Engineer. Brinell is noted as the creator of method for quantifying the surface hardness of materials, now known .dardized indentation hardness test was proposed by J.A. Brinell in 1900. His goal was to find a consistent and fast means of determining material hardness. The Brinell hardness test, still in .
Johan August Brinell was a Swedish metallurgist who devised the Brinell hardness test, a rapid, nondestructive means of determining the hardness of metals. In 1875 Brinell began his career . The first widely accepted and standardized indentation hardness test was proposed by J. A. Brinell in 1900. His goal was to find a consistent and fast means of determining . More than 100 years ago, Swedish engineer Johan August Brinell created a formula and procedure for determining the hardness of a metal and he showcased his prototype at the 1900 Paris Exposition, where talking films and .
Though loads of 500, 1000, 1500, 2000, 2500, and 3000 N are available in a typical Brinell hardness tester, a load of 500 N is used for testing relatively soft metals such as copper and aluminium alloys, while the 3000 N load is often used for testing harder materials such as steels and cast irons.However, the general rule is that the combination of test load and ball diameter . Around the same time as the Brinell was developing as a useful test the Scleroscope hardness tester was introduced as one of the first “non-marking” hardness-testing instruments. Albert F. Shore, who founded the Shore Instrument Manufacturing Co. in New York, and whose name is now synonymous with durometer testing, engineered the .
In 1875 Brinell began his career as an engineer at the Lesjöfers Ironworks and in 1882 became chief engineer of the Fagersta Ironworks. While at Fagersta he studied the internal composition of steel during cooling and heating and devised his hardness test, which was displayed at the Paris Exhibition of 1900. The test is based on the measurement of the impression left by a small, .An alternative method is the Brinell hardness test, which uses a hardened steel (or tungsten carbide) ball indenter with a diameter D of, usually, 10 mm.This is applied under a load P of 500–3000 kg applied for 10–30 s.The diameter of the circular indentation d is measured in millimetres. The hardness number, (HB) is calculated using the following equation: Brinell Hardness Test: Diagram of Brinell Hardness Testing Machine. Brinell Hardness Test is one of the most important hardness tests in the engineering industry and metallurgy. It is used when the surface of the metal is very rough to use another hardness test on it. There are two methods to perform the Brinell hardness Test on the metal as .Brinell hardness test is one of indentation hardness tests, that has been developed for hardness testing. In Brinell tests, a hard, spherical indenter is forced under a specific load into the surface of the metal to be tested. The typical test uses a 10 mm (0.39 in) diameter .
The Brinell hardness number is designated by the most commonly used test standards (ASTM E10-14[2] and ISO 6506–1:2005) as HBW (H from hardness, B from brinell and W from the material of the indenter, tungsten (wolfram) carbide).History of Hardness Testing. Early Hardness Testing. Hardness, as applied to most materials, and in particular metals, is a valuable, revealing, and commonly employed mechanical test that has been in use in various forms for over 250 years. . As an alternative to the Brinell, the Vickers hardness test was developed in 1924 by two gentlemen .
The first widely accepted and standardized indentation hardness test was proposed by J. A. Brinell in 1900. His goal was to find a consistent and fast means of determining material hardness. The Brinell hardness test, still widely used today, consists of indenting the metal surface with a 1 to 10 mm diameter ball at heavy loads of up to 3,000 kg.
These approximate relationships between hardness and tensile strength do not apply to nonferrous metals, with the possible exception of certain aluminum alloys. Related: Brinell Hardness Testing Equation. Table A Brinell Hardness to .The Brinell hardness HBW results from the quotient of the applied test force F (in newtons N) and the surface area of the residual indentation on the specimen (the projection of the indentation) after removal of the test force (see Brinell formula).To calculate the surface area of the residual ball indentation, the arithmetic mean d of the two perpendicular diagonals d1 and d2 (in mm) is . Brinell hardness test – a brief history. More than 100 years ago, Swedish engineer Johan August Brinell created a formula and procedure for determining the hardness of a metal and he showcased his prototype at the 1900 Paris Exposition, where talking films and escalators were seen for the first time. The Brinell test became established as the .
The Brinell hardness test was developed by the American Henry Brinell, who created the first tester in 1873. This is a widely accepted method in the field. The ASTM’s Brinell hardness test standard is used by alloy and metal suppliers and users, and it’s a basic requirement for all hardness testing equipment.A Vickers hardness tester. The Vickers hardness test was developed in 1921 by Robert L. Smith and George E. Sandland at Vickers Ltd as an alternative to the Brinell method to measure the hardness of materials. [1] The Vickers test is often easier to use than other hardness tests since the required calculations are independent of the size of the indenter, and the indenter .The Brinell hardness number (HB) is the load divided by the surface area of the indentation. The diameter of the impression is measured with a microscope with a superimposed scale. The Brinell Hardness Number HB is computed from the equation: where P is the applied load of 3,000, 1,500, or 500kg. D is the diameter of the ball in mm. (10mm)
The Brinell hardness test is commonly used to determine the hardness of materials like metals and alloys. The test is achieved by applying a known load to the surface of the tested material through a hardened steel ball of known diameter. The diameter of the resulting permanent impression in the tested metal is measured and the Brinell Hardness .ed to a hardness value. The Brinell test essentially introduced the production phase of indentation hardness testing and paved the way for additional inden-tation tests that were more relevant to different material types. Today, the Brinell test is often used for testing aluminum and copper al-loys at lower forces, and steels and castBrinell Hardness Test. Brinell hardness test is one of the indentation hardness tests developed for hardness testing. In Brinell tests, a hard, spherical indenter is forced under a specific load into the surface of the metal to be tested. The typical test uses a 10 mm (0.39 in) diameter hardened steel ball as an indenter with a 3,000 kgf (29.42 .
Brinell in 1920. August Brinell (10 October 1849 – 17 November 1925) was a Swedish metallurgical engineer.. Brinell is noted as the creator of a method for quantifying the surface hardness of materials, now known as the Brinell hardness test.His name is also commemorated in the description of a failure mechanism of material surfaces known as .
Brinell hardness test is a common method of testing the hardness of metals. Brinell hardness (HB) is a measure of the ability of a surface to resist penetration when an HB probe impacts it. The Brinell test method measures the indentation left on a specimen when the surface is hit with 20 high-pressure indents on a fixed area. Document History. DIS 6506-1. October 23, 2023 Metallic materials — Brinell hardness test — Part 1: Test method . This part of ISO 6506 specifies the method for the Brinell hardness test for metallic materials and is applicable up to the limit of 650 HBW. For specific materials and/or products, particular.
Brinell hardness testing is a commonly used method for determining the hardness of metals and alloys. The Brinell hardness test formula. When measuring hardness using the Brinell method, a hardened steel or carbide ball of known diameter under a known load is forced into the material being tested. The diameter of the indentation is then .The Brinell hardness is designated by the most commonly used test standards (ASTM E10-14 [2] and ISO 6506–1:2005) as HBW (H from hardness, B from brinell and W from the material of the indenter, tungsten (wolfram) carbide). In former standards HB or HBS were used to refer to measurements made with steel indenters.Concluding a hardness test using a popular method like the Brinell hardness test requires measuring the indentation left on the material surface by the load applied. Though several other hardness testing methods are available, the Brinell hardness test and how to read and represent its values are why we’ve written this guide.A Rockwell hardness tester. The Rockwell scale is a hardness scale based on indentation hardness of a material. The Rockwell test measures the depth of penetration of an indenter under a large load (major load) compared to the penetration made by a preload (minor load). [1] There are different scales, denoted by a single letter, that use different loads or indenters.
The test provides numerical results to quantify the hardness of a material, which is expressed by the Brinell hardness number – HB. The Brinell hardness number is designated by the most commonly used test standards (ASTM E10-14[2] and ISO 6506–1:2005) as HBW (H from hardness, B from brinell and W from the material of the indenter, tungsten . The Brinell hardness test is not suitable for very hard materials or hardened surface layers because the ball does not penetrate sufficiently into the material. Higher test loads are not the solution at this point, as this leads to deformation of the carbide ball. The flattening of the ball results in a larger indentation diameter and thus .
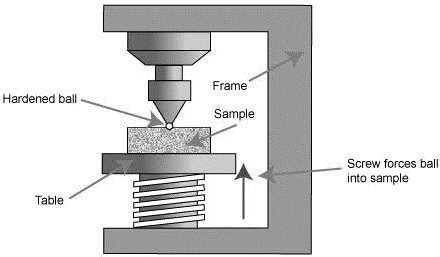
brinell hardness tester diagram
webTheresimmer 6fjdzcng Free Leaked Porn Videos
brinell hardness test history|brinell hardness test example